ESnet Launches Cloud Connect Service to Support Scientific and Enterprise Workloads
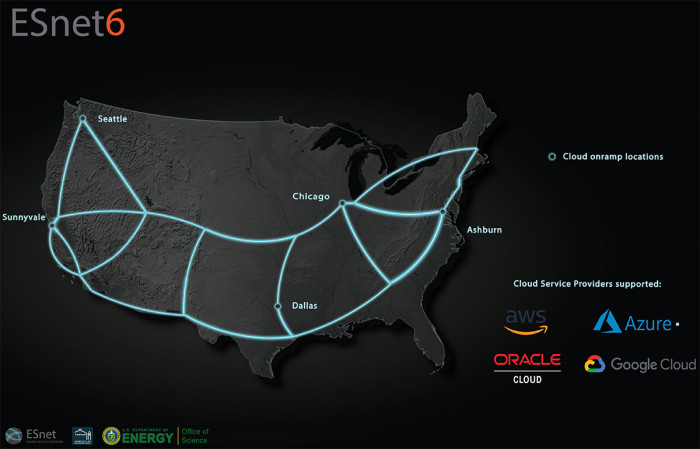
Diagram of ESnet6's current cloud peering points (enlarge)
Part of managing a network dedicated to handling vast swaths of scientific data is also ensuring it adapts to trends for how data is being created, stored, and computed. A pattern has emerged in recent years allowing for access to elastic and scalable systems on demand. Nebulously titled “The Cloud,” it refers to software and services that run over the public internet. For ESnet, this is just another place where science intends to happen.
To drill down more on the nebulosity of the term “The Cloud,” there are different flavors of how the services/software are consumed. "Public Cloud" refers to services and software that are open for all users and subscribers around the world: for example, those provided by Dropbox, Slack, Salesforce, and Office 365. Meanwhile, as its name suggests, a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is an environment in which all virtualized hardware and software resources are dedicated exclusively to, and accessible only by, a single organization. The intention of a VPC is to emulate the on-premise data centers of old while removing the headaches of managing their physicality (space and power constraints), and offering the added benefit of instantaneous access to scale when needed. Although some organizations decided to go all-in on the new virtual environments by harnessing a cloud-native posture, some took a more measured approach by seamlessly blending their on-premises infrastructure with the new virtualized territory, in a format also known as a hybrid cloud.
As usage of virtual private clouds grew, it became apparent that connectivity over the public internet was too unreliable, slow, and insecure: dedicated, high-bandwidth connectivity was a must-have. In response, every major Cloud Service Provider (CSP) launched an offering. Amazon Web Services (AWS) was first, launching “Direct Connect” in 2012; Azure followed in 2014 with its “ExpressRoute”; and in 2017, Google launched Cloud Interconnect. (Read more about the history.)
These virtual circuits are the driver behind the new ESnet Cloud Connect service aimed at supporting both scientific and enterprise workloads. The goal is to carve out a dedicated, high-bandwidth path (up to 10 Gbps) across ESnet’s 400GE-capable backbone from any supported user facility to the nearest cloud on-ramp by utilizing two interim network service providers: Packet Fabric and Equinix. From there, ESnet would help provision the major CSPs’ (Azure, AWS, GCP) aforementioned flavor of dedicated connectivity into your Virtual Private Cloud.
This solution is designed to scale from simple dedicated connectivity and a singular cloud provider to a virtual routed network utilizing multiple cloud providers, onramps, and interconnecting user facilities. This series of blog posts will focus on a few suggested use cases for utilizing ESnet’s new service offering. For questions or to learn more, email Joshua Stewart.

